Table of Contents
Preface:
Are you deciding on starting your career in SAP MM?
Have you worked on where you will send your resume for a job?
Are you worried about what questions the interviewer might ask?
Then, fear not, for I am here to aid you in your quest!
I have done the research work and listed below the Top 25 SAP MM Interview Questions and Answers for you.
Before beginning with the list, let me share a piece of advice with you- Wear confidence when you go for an interview.
Marcus Garvey, a Jamaican-born Black nationalist and leader, once said,
“If you have no confidence in self, you are twice defeated in the race of life.”
Most of us break out in a cold sweat when it comes to giving an interview. But if you prepare well and go with a calm mind, believing in yourself, you can ace the interview.
Just remember that if you do not know the answer, be honest and tell that you are unaware of its reply. It is understandable to be not an all-knowing individual.
So, let us learn the Top 25 SAP MM Interview Questions and Answers.
Q.1. Give a brief introduction of yourself.

Ans.Whensoever you go for an interview, always prepare a brief and crisp introduction of your working experience, skillset, and achievements that you want to highlight to your interviewer.
Note down the essential highlights, such as skills you have gained from your previous job that will serve as an asset to your new role, and rehearse it before the mirror. Doing this exercise will enable you to practice your interview session and build confidence.
Start with giving an introduction about yourself, your personal life in one or two sentences.
Then share about your education and any significant achievements in college or school. Then draw attention to your work experience, any achievements, and skills gained during that period. You can also highlight how your skillset can be beneficial for your new role and help the company achieve its goals.
After asking some questions about you and your personal life, the interviewer will move towards the next set of questions asking some basics of SAP MM.
Q.2. Give a brief meaning of SAP.
Ans.SAP is an acronym for Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing. It is a software and a company of German origin, developed by Wellenreuther, Hopp, Hector, Plattner, and Tschira in 1972. Initially, SAP was an abbreviation of System Analysis Program Development. The purpose of designing SAP was to provide solutions for managing business processes and customer relationships. It is a No. 1 software in the ERP (enterprise resource planning) market.
Q.3. What is your understanding about SAP MM?

Ans.MM stands for Material Management. It is a functional module (a module is nothing but a business process) in SAP. SAP MM deals with the process of procurement or purchasing and material management. SAP MM is the basics of logistics that consists of modules such as Sales and Distribution, Production Planning, Warehouse Management, Plant Maintenance, etc. The module of MM consists of master data, system configuration, material valuation, material requirement planning, etc.
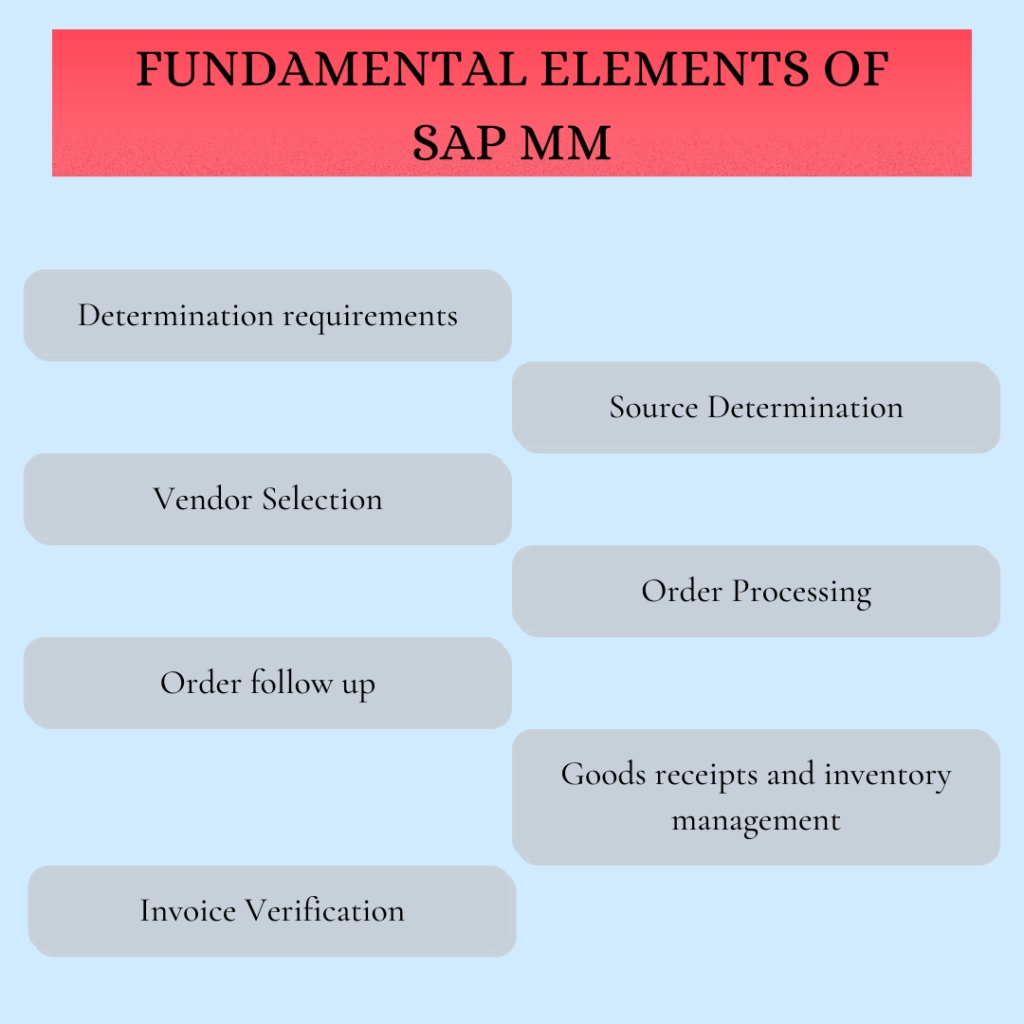
Q.4. Name some of the fundamental elements in SAP MM.
Ans.The fundamental elements of SAP MM are:
- Determination requirements
- Source Determination
- Vendor Selection
- Order Processing
- Order follow up
- Goods receipts and inventory management
- Invoice Verification
Q.5. Explain the role of the SAP MM module in business.
- Ans.SAP MM plays a significant role in the Logistics domain of an organization in which it handles procurement activities.
- It also assists in material management processes such as planning, purchasing, controlling, etc.
- It also serves as an interface between Logistics and Account Payable.
Q.6. List some of the advantages of SAP MM.
Ans.The advantages of SAP MM includes:
- Multi-Location inventory
- Cost Minimization
- Product Life Cycle Management
- Bin Management
- Scheduling and resourcing
- Inventory Replenishment
- Material Valuation
Q.7. How many types of stocks are there in SAP MM? Name them.
Ans.There are three types of stocks in SAP MM. The name of these stocks are:
- Valuated Stock- Valuated stocks can be defined as those stocks that are valuated at the plant level.
- Non-Valuated Stock- Non-valuated stocks are those stocks that are used for consumption in bulk and have low costs, such as screws, washers, pins, etc.
- Special Stock- Special stocks are those stocks that are available but not owned by customers. Special stocks cannot be stored in a facility. Examples of such stocks include consignment, sales order, project stock, etc.
Q.8. Name the types of stocks available in valuated stock.
Ans.The sub-types of stocks included in valuated stocks are:
- Unrestricted Stock- Unrestricted stocks are those stocks that are ready for use and available at hand in the facility.
- Quality Inspection Stock- Quality inspection stocks are those delivered materials that are retained to check or inspect the quality.
- Blocked Stock- The materials that come under blocked stocks are those found to be of bad quality. The material is found to be of poor quality during production when some irregular functionalities get detected in the material.
Q.9. Name the types of stocks available in special stock.
Ans.The sub-types of special stock includes:
- Subcontracting
- Consignment
- Stock Transport Order
- Third-Party Processing
- Returnable Transport Packaging
- Pipeline Handling
Q.10. Define consignment stock.
Ans.Consignment stocks are those stocks that are provided by vendors and kept in the company’s storage area. These stocks are available for use with the vendor still being the owner of it. The company can withdraw material from these stocks for use by paying for it to the vendor.
Q.11. Enlist prerequisites for creating a purchase info record.
Ans.The prerequisites required for creating a purchase info record are:
- Material Number
- Vendor Number
- Manufacturer Part Number (MPN)
- Organizational level code
Q.12. Briefly define the terms Planned delivery and GR Processing Time.
Planned Delivery Time (PDT) is a tool in SAP ERP used to update the time of scheduled delivery. It shows the number of calendar days for obtaining the material.
GR Processing Time reflects the number of workdays consumed for inspection and storing after the material is received.
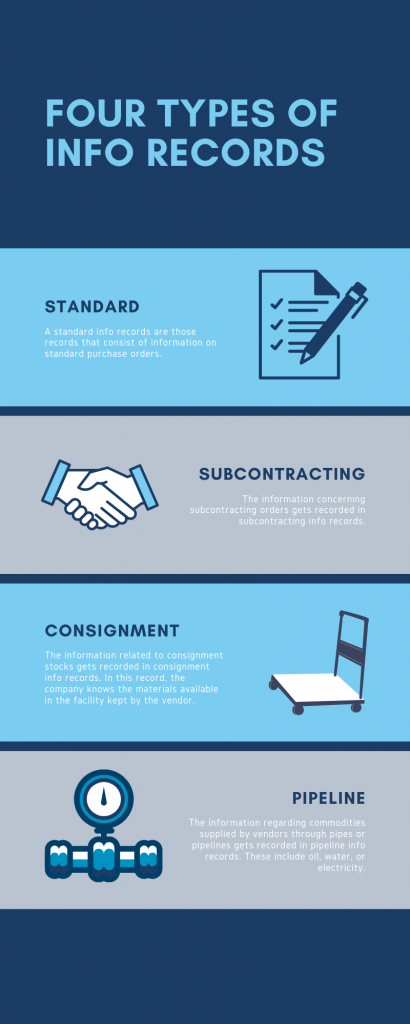
Q.13. How many types of info records are there? Briefly define them.
Ans.There are four types of info records. They are:
- Standard- A standard info records are those records that consist of information on standard purchase orders.
- Subcontracting- The information concerning subcontracting orders gets recorded in subcontracting info records.
- Consignment- The information related to consignment stocks gets recorded in consignment info records. In this record, the company knows the materials available in the facility kept by the vendor.
- Pipeline- The information regarding commodities supplied by vendors through pipes or pipelines gets recorded in pipeline info records. These include oil, water, or electricity.
Q.14. Explain what is Material Requirement Planning (MRP)?
Ans.In SAP ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), Material Requirement Planning (MRP) is a planning tool that helps procurement and production planners to create practical and realistic plans. Once the planners create a plan, the initiation of production and procurement plans gets formulated.
Q.15. Define Consumption-Based Planning (CBP)?
Ans.Consumption-Based Planning (CBP) is planning that uses the history of consumption values. By using consumption values, requirements are forecasted. Consumption-Based Planning (CBP) gets activated once the stock level plunges below a fixed reorder point or forecast requirements are assessed based on the history of consumption values.
Q.16. Differentiate between MRP and CBP.
Ans.In Material Requirement Planning (MRP), requirements of materials are forecasted on the basis of sales and operations planning. However, in Consumption-Based Planning (CBP), requirements of materials are predicted on the basis of the history of the demand for materials.
Q.17. What is your understanding about the Master Production Schedule (MPS)?
Ans.Master Production Schedule or MSP can be defined as a plan laid out by a company for the production, staffing, inventory, etc., for individual final articles. In this scheduling, the company plans which product and its related quantities get produced during a period. Usually, this period spans between 3-18 months. The data used as an input in the Master Production Schedule include forecast demand, production costs, inventory cost, etc.
Q.18. Define Purchase Order and Production Order.
Ans.The purchase order can be defined as a formal instruction given by a purchasing firm to a supplier, requesting to supply materials in certain quantities and on a particular date.
However, a Production order specifies the work center or resources that need to be used in material manufacturing. A production order is a request made by the company to manufacture a particular quantity of material or carry out a particular activity on a specific date. This type of order is helpful for production planning.

Q.19. Explain what is Master Data?
Ans.Master Data can be defined as the core data that serves as a base for any transaction. Master data is produced while performing any activity such as producing, transferring stock, selling, purchasing, etc. Examples of master data are Material Master Data, Vendor Master Data, Customer Master Data, etc.
Q.20. Define RFQ.
Ans.RFQ is a short form for Request For Quotation. RFQ is a request sent to dealers or vendors asking them to submit quotes presenting prices and terms and conditions. An RFQ also gives details about the date of delivery, goods and services, quantity, and submission date.
Q.21. What do you mean by process order in SAP MM?
Ans.Process Orders (PP-PI-POR) are the core elements that are used to plan and execute process manufacturing in detail. The process order defines the production of materials in batches in the cycle of production.
Q.22. How many types of Basic Procurement are there? Name them.
Ans.There are two types of Basic Procurement.
- Procurement for Stock vs. Procurement for Direct Consumption.
- External Procurement vs. Internal Procurement.
Q.23. Define MIRO.
Ans.MIRO stands for movement in receipt out. MIRO handles the invoice verification activities of the bills raised from the dealer’s end.
Q.24. Define MIGO.
Ans.MIGO stands for movement in goods out. MIGO is used for the goods that are moved from one plant level to another plant level, goods receipt, transfer from one storage location to another storage location, etc. The logistics department uses the term MIGO.
Q.25. What do you understand about RFI and RFP?
Ans.RFI stands for Request for Information. RFI is used in the business processes where written information is assembled concerning the competencies of sellers.
RFP stands for Request for Proposal. RFP is sent by companies to potential sellers asking for business proposals.
Conclusion:

These are a few questions that an interviewer can ask you while interviewing you. In addition to these questions, I request you to go through definitions of terms such as subcontracting, stock transport order, third-party processing, returnable transport packaging, pipeline handling, and other important words. Remember that these are just a few questions from the plethora of topics under SAP.
Go for the interview in formal attire. For men, I advise that you have a clean and short haircut. And for women, either wear a ponytail with all strands tied cleanly in a rubber band or make a simple bun.
Hopefully, this article will help you ace your interview successfully and land you your dream job!
I wish you all the best and great success in your career.
Recommended Reads
- 10 Best SAP Training Institutes in India
- Top 15 SAP FICO Courses in Hyderabad with SAP Jobs for Freshers
- Top 35 SAP FICO Interview Questions and Answers
- 15 Best SAP HR Courses In India
- Best 10 SAP Training Institutes in Delhi
FAQs:

Ans.The best institute that offers SAP MM courses in India is Henry Harvin Education. Henry Harvin Education is one the top-ranking institutes for offering those courses that upskill you. Many prestigious companies like Aaj Tak, India Today, McAfee, SAP, and more.
You can apply for the SAP MM course by clicking on the link.
Other SAP courses offered by Henry Harvin are listed below.
SAP FICO Training Course
SAP HR Course
SAP HANA Course
Ans.Some career options available after the completion of the SAP MM course are:
a. SAP MM Consultant
b. Team Leader
c. SAP MM Plant Maintenance analyst
d. SAP MM functional Configurator
e. SAP Functional Analyst in MM
Ans.An SAP MM Consultant, as per statistics, earns up to INR 5.5 lacs on average.
Ans.The roles and responsibilities performed by an SAP MM Consultant are:
a. Looking into businesses through the eyes of Purchasing and Inventory departments.
b. Planning of customer business processes.
c. Instruct operators to use the SAP system.
d. Improve operational and analytical reports for consumers.
Recommended Programs
SAP FICO Course Training
With Certification
SAP FICO Course: Ranked Amongst Top 3 Courses | Recognized by Govt of India | Award Winning Institute | ISO 29990:2010 Certified | Live Online Instructor-led Certified SAP FICO Training & Certification
SAP FICO S/4 HANA Course Training
With Certification
SAP FICO Course: Ranked Amongst Top 3 Courses | Recognized by Govt of India | Award Winning Institute | ISO 29990:2010 Certified | Live Online Instructor-led Certified SAP FICO Training & Certification | Qualify for SAP FICO Certification and Develop a Promising Career in the Field of SAP FICO | 100% Practical Training Method | Training on S/4 HANA Software.
SAP HR ECC Training Course
With Certification
Recognized by Govt. of India | Award Winning Institute | ISO 29990:2010 Certified | One of the most Fundamental Modules of SAP ERP System | Develop a Promising career in the field of SAP HR | SAP HR application module supports the procurement and inventory functions
SAP Security Training Course
With Certification
Leading ERP in the Industry in the most important aspects of current business | Get Introduced to SAP R/3 Architecture, User Administration and SAP Authorization objects | Gain extensive knowledge of SAP Authorization, User Master Records, Profile generation using PFCG
Explore Popular CategoryRecommended videos for you
SAP FICO Course by Henry Harvin®
Ranks Amongst Top #5 Upskilling Courses of all time in 2021 by India Today
View Course









.webp)
