Table of Contents
What is Digital Literacy?
Let’s have a look at the case of Smita to understand.
Smita teaches at ABCD International School in Pune. Her sister, Rani, is also a teacher and works for Girl’s High School, Bilaspur. They both have the same job description. Smita develops her lesson plans, worksheets on the computer, she takes help from various sites and apps. She shares these things through an app. She can refer back, easily, to her work whenever she wants. Her sister develops all these things in hard copy and has a pile of paper rammed into her desk drawer. She hands it over to the student when she meets them in class. If she wants to refer back, it becomes a cumbersome business for her.
In the former case, we see that the work is digitalized and, in the latter case, is not. To work on digital media, we need to have knowledge about the topic as well as the usage. This acquaintance with the functioning of digital media, is called digital literacy.
Literacy means reading and writing skills. There was a time in history when we were formulating policies and working for literacy. Still, we have some more distance to travel before we achieve our goal of 100% literate India. Suddenly a tremendous development occurred in the Information and Technology sector, and now with the advent of the internet and with globalization, a certain segment of this massive population has tread forward and is motivated to be digitally literate. The word digital tacked before literacy, changes the meaning. ‘Digital’ is an elaborate topic, but in short, it is something that deals with technology.
According to the American Library Association’s task force,
“Digital literacy is the ability to use information and communication technologies to find, evaluate, create, and communicate information, requiring both cognitive and technical skills.”
Digital literacy has been explained more simply by Hiller Spires, a professor of literacy and technology at North Carolina State University, as having three aspects
TEFL Certification in India
45-min online masterclass with skill certification on completion
Mentored By Chetan Bhagat
$99 FREE
Access Expires in 24Hrs

Upcoming Batches of TEFL Course :-
| Batch | Mode | Price | To Enrol |
|---|---|---|---|
| Starts Every Week | Live Virtual Classroom | 26500 | ENROLL NOW |

- Finding and Consuming Digital Content – Finding content happens when you go through the search engines, type out the keywords, and sift through a lot of available data and then find out what is relevant for you.
Once you find out what you were looking for you, read through it. But passive reading on any gadget is equivalent to reading from a book. This reading or article, when stacked with hyperlinks, videos, audio clips, images, interactive graphics, share buttons, or a comments section, requires you to use your technical skills and intelligence to make a decision. This makes the two readers different from each other. How much you stray away from your landing/initial page differs for each reader.
- Creating Digital Content – The next aspect is creating content. It enhances the skills to prepare responsible content in the form of emails, tweets, podcasts, videos, etc. These require mature thinking, as digital content is often meant to be shared. It also requires creativity and knowledge of various digital tools.
- Communicating or Sharing it – Digital content is usually meant to be shared. Communicating digital content needs to be guided properly to have the proper impact as it also saves the person sharing it from any kind of danger. The content needs to be such as it doesn’t attract any kind of dangerous controversy and puts the person’s privacy, safety, and reputation at stake. The consequence of the matter shared should be thoroughly interpreted before communicating it.
Here is a short video for understanding Digital Literacy better:
Digital Literacy is Important for Teachers.
The modern generation is marked with a quality called ‘speed,’ and nobody has patience.
The proverb, ‘slow and steady wins the race’ has lost its significance.
Gadgets and gismo surround Their life. The teachers who shoulder the major responsibility of imparting education to this generation have to match up to the expectation of these fast-paced young netizens.
Information, if not conveyed properly, may have disastrous results. Young learners are exposed to the digital world at a very early age, but they should also be taught to handle it properly and manage to extract the essence of knowledge available digitally. Teachers play an important role in this.
The teachers of today’s generation must equip themselves with the digital skills necessary to help their students become responsible digital citizens.
Read Also: TEFL Vs TESOL
Here we will walk through a few motives why digital literacy is important for teachers:
1. Optimal Usage of Search Engines Like ‘Google’

Modern students who have access to an internet connection and even a smartphone can find answers to all kinds of questions, whether simple or complex. But they may not understand the answers. They are also not aware of the genuineness of the information or the source.
It is the digitally literate teacher’s responsibility to guide the students regarding which sources are authentic and which are updated regularly or whether there are other useful sites linked to the subject and, more importantly, the piece of information is written in biased language or objective.
It is the educator who inspires the student to be creative and prompt deep thinking and logical analysis among students. In this way, the students come out with original ideas and their answers. The teacher should encourage students to have an all-around knowledge of the software, which is relevant.
2. Teaching Learners to be Ideal Digital Citizens
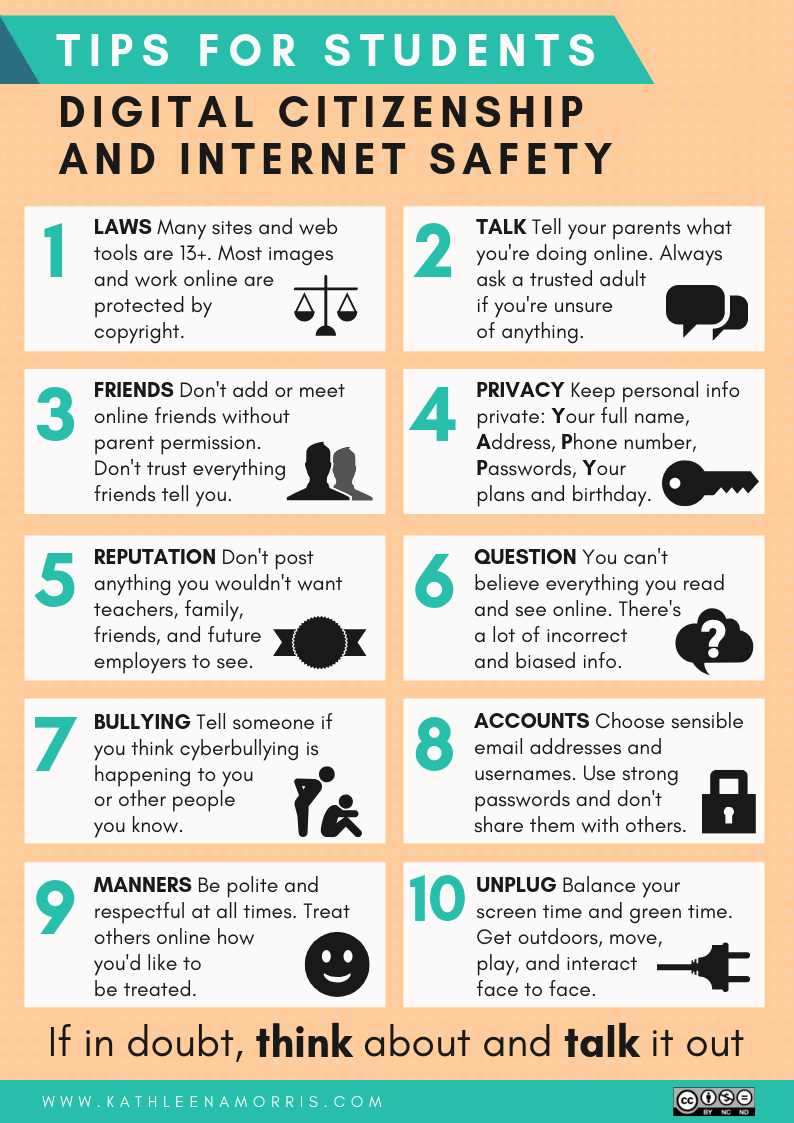
Young people are taught by their elders to grow up and become responsible citizens of a country. Similarly, the web world also requires accountable citizens so that it develops healthily. With the increase in the number of people using the digital space for various reasons, there are strong chances of illicit activities taking place. The students may also fall prey to such activities as either victims or offenders (as they lack enough knowledge).
Here again, the teacher plays a major role. He/she can guide and motivate their students to be responsible digital citizens. In general, two major issues surface in the case of education-related digital misuse; academic plagiarism and cyberbullying.
Academic plagiarism occurs because of random copying and sharing of information from the digital world. The student may even do it unknowingly or without having a proper understanding of the issue of plagiarism. In this case, the teacher should discuss plagiarism at the beginning of the session and lay down strict rules.
Cyberbullying is a prevalent deviant behavior among students. Bullying itself is a major concern in schools or educational institutions in the 21st century. This irresponsible behavior surfaces in the electronic media as well. Students should be deterred from engaging in such activities, and those bullied must be given proper counseling.
Must Check US Ranked No. 1 TEFL Certification Course Online
3. Minimizing the Digital Divide

Our country is a developing country with a huge population, resulting in social and economic stratification. Therefore the development of technology, which is acting as a boon for e privileged few, does not reach a large percentage of potential learners. This causes a divide. The digitally literate teacher can advocate for the cause and help the government find a solution to such an intrinsic problem.
4. Motivating Proper Usage of Digital Media
Students are proficient in using various apps and sites very well. But in many cases, they are not able to fathom the potential of the app. It is the responsibility of the teacher to help students use their digital knowledge appropriately.
For example, children use Instagram to post photographs but never think of using it for their projects. They use TikTok and similar apps to upload insensible stuff but never think of using it as a journalism tool or showcase best practices.
5. Positive Discrimination of Students and Choosing the Correct App or Tool for Teaching

A digitally literate teacher can use various available apps and information to impart better and elaborate education. Keeping in view the different students, the teacher can devise lesson plans and mode of delivery that is best suited to an individual student. A student who gets easily distracted can be shown visuals, if someone is more comfortable in hearing what the teacher says, he /she can be provided audio clues. Similarly, the teacher can share information based on individual needs, thus making use of technology.
A digitally literate teacher knows his/her class properly, and in cases when the school management forces irrelevant apps or culture-specific programs to be included in classroom teaching, the sensible teacher may logically explain the pros and cons of using such a tool.
6. Improving Technology
Digitally literate teachers can give crucial suggestions to education-based technology developers on pedagogical practices or specific subjects. This enhances the quality as well as the quantity of useful data for educational purposes. Digitally educated teachers can even share their expertise with their peers, thus upgrading the teaching standards.
Status of Digital Literacy in India
India, as we all are aware, is blessed with a huge population. It is a herculean task for the government to keep up with the development of such a diversified country. In our country, which has just started climbing up the ladder of development, struggling to take a step forward, digital literacy is a distant dream. We have almost 40% of the population below the poverty line, the general illiteracy rate itself is 25 to 30%, and digital illiteracy is more than 90%.
However, the world outside is undergoing a profound change, scientists and technologists are gearing up for the future of digitization. UNESCO, as a monitoring indicator of its Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG4), urges the countries to keep digital literacy. Nonetheless, the government is trying to do its bit to provide the citizens with the enormous benefits of digital literacy.
The government launched the Digital India campaign in 2015, but it had has its share of challenges like inadequate infrastructure, low bandwidth, non-availability of computers. Therefore, we need to review the planning for optimizing the digital India campaign and motive.

- We first need to clarify what essentially is meant by ‘Digital Literacy’!
- Once the target is set, we need to give a direction to it. Maybe we should frame a strong policy, keeping in view the situation in our country. And the private sector should also be involved.
- Next, we should motivate the creation of content for digital media. The intelligent Indians are capable of and are at present, creating a lot of content.
- A proper record should be maintained regarding digital literacy in government offices and, more importantly, in educational institutions.
- And lastly, we need to keep track of the young digital citizens and guide them to consume content thoughtfully and be creative.
After reviewing the status of India’s digital literacy rate we can conclude that we have a long way to go, none the less we cannot forget our achievements and see the other side of the picture. Our education system has been revamped, and Information technology has been introduced as an important subject. Computers have been made available to many underprivileged schools to make our rural population digitally literate. To make this development forward, we need to focus on making our teachers digitally literate.
Digitally Literate Teachers in Modern-Day Schools.
The teachers have been vested with the responsibility of all-around development of students. Therefore they keep themselves updated always. Many urban schools have brought in digital technology to be used regularly for the delivery of lessons. Smart classes with various education apps have been installed to make learning easy and fun. The teachers have updated themselves in using digital media to prepare lessons, worksheets, and even question papers and mark sheets.
Online teaching is becoming a normal phenomenon, and teachers tend to become more innovative and put in extra efforts to create interactive classes with video and audio clips.
We have seen that this digital literacy has helped during the recent lockdown due to the deadly Coved – 19.
Role of Digital Literacy among teachers and students during this pandemic
The deadly COVID 19 has locked the world in their homes. Everything came to a halt, except medical, banking, transportation of essential goods, vital services, law and order, and partly the education sector. During these difficult times, certain schools showed how to utilize their time efficiently by holding online classes on various meeting apps (Zoom, Microsoft teams, Cisco WebEx). This was made possible by the digital literacy of teachers and students alike. Teachers exhausted their time and energy, preparing interactive sessions, and the students responded enthusiastically.
Major Concerns About Digital Literacy in India

- Though there have been some efforts to impart digital education to teachers, there is a dearth of computer teachers in rural areas. A certain village in Odisha has 18 computers, but only 10% is computer literate as there is no teacher there.
- Many children have the privilege of getting exposed to digital media, and they tend to learn using it without formal training. In the process, they may harm themselves. So proper digital safety measures need to be taken. Teachers can only teach this.
- The digital divide is a major concern in the Indian scenario where there is a wide disparity in economic conditions.
To Sum Up

Imparting education online is not new. The world is undergoing rapid change, and for almost a decade, digitalization of all sectors is being emphasized. The education sector was also revamped in the light of the newfound knowledge and has been a boon to many.
A study by the Centre for communication and development studies of a school in Uttarahalli, Bengaluru, presents an encouraging picture of the integration of technology in education by digitally literate teachers. This school is considered a model in contrast to the lack of motivation, a conviction of the positive impact on education, and infrastructure in many schools.
The teachers here were self-motivated to impart education using digital media. They have 15 desktops, 18 laptops, and six tablets. Learning Links, Educomp, and the Dell Youth Connect Programme. The teachers receive both formal (from the Educomp and Learning Link resource persons) and informal training (they share their experiences among themselves). They feel imparting daily lessons, remedial classes, etc. are easy as students, for example, understand ppts better as they are to the point. Moreover, the teachers themselves feel empowered, though they initially felt it to be a burden and thought of digital media only as a source of entertainment, with children taking more interest in digital learning methods, the teachers were inspired to put in more hours and upgrade themselves.
All schools must work in this way, and now NCERT has introduced a digital safety curriculum for schools. Soon, we will see our digitally literate teachers building the pathway towards a digitally educated India who has full knowledge of digital etiquettes and as responsible digital citizens.
However, India still has to improve on infrastructure. But we must not lose hope, and we should help our brethren as we all are part of this great nation. A smart blend of online and offline teaching can help in bridging the digital divide. With the growing use of smartphones by all categories of people can also help in serving as a tool to provide digital literacy. Moreover, modern-day youth is aware that digital literacy places them in a better position to earn a job.
Kofi Annan(former Secretary-General of the United Nations and Nobel laureate) had once stated, “Literacy is a bridge from misery to hope. It is a tool for daily life in modern society. It is a bulwark against poverty and a building block of development… Literacy is, finally, the road to human progress and the means through which every man, woman, and child can realize his or her full potential.” This is very much applicable in the case of digital literacy as well.
Check Out our highly recommended TEFL Certification.
Recommended Reads:-
Also Check this Video:-
FAQs
Ques 1. What is digital learning exactly?
Ans. The abilities that prepare someone to live, learn, and work in a digital society through innovation and cooperation.
Ques 2. What are the advantages of digital literacy?
Ans. Digital literacy helps students and teachers progress academically. As a result, pupils efficiently employ digital technologies in various aspects of their lives.
Ques 3. What courses are offered as part of digital literacy programs?
Ans. DLC includes five courses from the Digital Literacy program: ACC, BCC, CCC, CCC+, and ECC.
Ques 4. What is the relationship between digital literacy and English language learning?
Ans. Using search techniques and digital collaboration can be difficult in a foreign language. It is therefore made easy by incorporating Digital Literacy development in the English language sessions.
Ques 5. Does reading online articles contribute to digital literacy?
Ans. Reading articles on the internet isn’t enough. Digital literacy training helps people obtain the digital skills needed to participate in the digital economy and improve their lives.
120-hours TEFL / TESOL Online Certification Course
Ranked No. 1 Course | 100% interview guaranteed | Live Online Instructor-led TEFL Training & Certification | AAEFL Certified TEFL Course
View Course
Recommended Programs
120-hours TEFL / TESOL
Online Certification Course
Ranked No. 1 Course | 100% interview guaranteed | Live Online Instructor-led TEFL Training & Certification | AAEFL Certified TEFL Course | Qualify for 12,000+ jobs from 6+ countries | With over 100,000 English teaching positions opening every year, immerse into the market of 2 Billion English learners today.
TEFL Certification Online
Course in USA
Ranked No. 1 TEFL Certification Course in USA | 100% Interview Guaranteed | Online Certification course in USA | instructor-led training and certification program of TEFL | Qualify for 12000+ jobs from 6+ countries.
Post Graduate Program
in TEFL
Ranked No. 1 Course | 100% interview guaranteed | Live Online Instructor-led Post Graduate TEFL Training & Certification | AAEFL Certified Post Graduate Program in TEFL | Qualify for 12,000+ jobs from 6+ countries | With over 100,000 English teaching positions opening every year, immerse into the market of 2 Billion English learners today.
Explore Popular Category




![Top 10 Countries for Teaching English Abroad in 2024 [Updated]](https://hh-certificates.sgp1.digitaloceanspaces.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/10105810/pasted-image-0-15-270x180.jpg)
![What is EFL? How does EFL differ from ESL? 2024 [Updated]](https://hh-certificates.sgp1.digitaloceanspaces.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/24123609/pasted-image-0-18-270x180.jpg)
![Ten Top TEFL Course in Idaho in 2024 [Updated]](https://hh-certificates.sgp1.digitaloceanspaces.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/09120053/blog429-270x180.jpg)

.webp)
